before
centos 7.4 + python 3.6.8 + pip 9.0.3 + wheel 3.1.0
关于Python包管理工具的发展和使用本次共整理为三篇:
- 第一篇主要要概述Python包管理工具的发展史,以及各包管理工具的简单使用。
- 第二篇(即本篇)则是主要介绍包(模块)的分发,也就是如何将你的包打包,然后分发给别人使用。
- 第三篇则是主要研究在包分发时,如何加密你的源码,防止源码泄露。
有失误或者引用链接不可用时,多多包涵,也欢迎留言斧正。 开始吧!
再来强调一些东西,想要制作whl文件,需要下载wheel模块支持:
pip install wheel
pip install wheel==3.1.0
pip install https://pypi.doubanio.com/simple wheel==3.1.0你应该考虑的规范 因为whl文件可以上传到PYPI,所以,有些规范你要在制作whl文件的时候要注意,比如说要有:
- README:提供包的基本描述和使用方法。
- LICENSE:版权信息。
当然内部使用的时候,可以省略不写。
重中之重:setup.py文件 除此之外,包内要有一个重要的setup.py文件,该文件主要使用setuptools的setup模块,提供打包所需要的基本信息。python依赖此脚本中的配置信息,将相关模块、静态文件,打包成一个完整的模块安装到site-packages文件。 所以,我们要重点研究下这个文件。
先上我的包目录结构:
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# tree
.
├── setup.py
└── wellcommon # 模块包
├── com4gps.py
├── com.py
├── encrypt # 子目录,这也是一个重点
│ ├── helper4encrypt.py
│ ├── __init__.py # 千万别忘了 __init__.py
│ ├── py_apply.py
│ ├── wzipfile.py
│ └── zxzn_dll
│ └── raspberrypi4B
│ ├── libz.so
│ ├── libz.so.1
│ ├── libz.so.1.2.11
│ └── libzxzn_dll.so
├── helper4file.py
├── helper4str.py
├── __init__.py # 千万别忘了 __init__.py
├── log.ini
├── log.py
├── MANIFEST
├── README.txt # 要是不上传什么PYPI,可以不写
└── wcv.py
4 directories, 19 files注意setup.py文件必须有且必须和包同级。 再来看setup.py文件中一些重要的参数:
from setuptools import setup
# 需要将那些包导入,注意,必须写包名,和包内的子目录,写法如下,普通的py文件无需写
packages = ["wellcommon", "wellcommon.encrypt"]
# 如果有静态文件,这么导入即可
# file_data = [
# ("smart/static", ["smart/static/icon.svg", "smart/static/config.json"]),
# ]
# 第三方依赖
# requires = [
# "pandas>=0.23.4"
# ]
# 自动读取version信息,我这里没有,你可以参照
# about = {}
# with open(os.path.join(here, 'smart', '__version__.py'), 'r', 'utf-8') as f:
# exec(f.read(), about)
# 自动读取readme
# with open('README.txt', 'r', 'utf-8') as f:
# readme = f.read()
setup(
# name=about["__title__"], # 包名称
name='wellcommon',
# version=about["__version__"], # 包版本
version='1.0', # 包版本
# description=about["__description__"], # 包详细描述
# long_description=readme, # 长描述,通常是readme,打包到PiPy需要
# author=about["__author__"], # 作者名称
author='张开', # 作者名称
# author_email=about["__author_email__"], # 作者邮箱
author_email='xxxx@qq.com', # 作者邮箱
# url=about["__url__"], # 项目官网
url='https://www.cnblogs.com/Neeo/p/10864123.html', # 项目官网
packages=packages, # 项目需要的包
# data_files=file_data, # 打包时需要打包的数据文件,如图片,配置文件等
# include_package_data=True, # 是否需要导入静态数据文件
python_requires=">=3.0, !=3.0.*, !=3.1.*, !=3.2.*, !=3.3*", # Python版本依赖
# install_requires=requires, # 第三方库依赖
zip_safe=False, # 此项需要,否则卸载时报windows error
classifiers=[ # 程序的所属分类列表
'Development Status :: 5 - Production/Stable',
'Intended Audience :: Developers',
'Natural Language :: English',
'Programming Language :: Python',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.4',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.5',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.6',
'Programming Language :: Python :: 3.7',
'Programming Language :: Python :: Implementation :: CPython',
'Programming Language :: Python :: Implementation :: PyPy'
],
)上面的实例还是比较全的,setup函数中的重要参数:
- name:写成啥后续生成的报名就是啥。
- version:也会展示在生成whl名中。
- 作者信息之类的,看你自己了。
- packages:我认为非常重要的参数,如果你的包中有子目录,就要按照上述例子中的写法列出,不然容易出问题,当然要是包中都是
py文件,可以不写该参数。 - 其他的什么url、requires就看具体情况而定了。
现在,基本配置倒是都完了,具体有没有问题,要打包的时候才知道。
制作过程
- 首先检查
setup.py文件写的有没有什么问题,有问题的会在给你提示处理来的,没有问题就不报错,也没提示,如下,就是没有问题的。
[root@r zhaopeng]# python3 setup.py check
running check
[root@r zhaopeng]#使用check命令来检查,发现没有提示和报错,往下走。
- 打包:
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# python3 setup.py bdist_wheel
running bdist_wheel
running build
running build_py
creating build
creating build/lib
creating build/lib/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/wcv.py -> build/lib/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/log.py -> build/lib/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/com4gps.py -> build/lib/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/__init__.py -> build/lib/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/helper4file.py -> build/lib/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/com.py -> build/lib/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/helper4str.py -> build/lib/wellcommon
creating build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt
copying wellcommon/encrypt/wzipfile.py -> build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt
copying wellcommon/encrypt/py_apply.py -> build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt
copying wellcommon/encrypt/__init__.py -> build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt
copying wellcommon/encrypt/helper4encrypt.py -> build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt
installing to build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel
running install
running install_lib
creating build/bdist.linux-x86_64
creating build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel
creating build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
creating build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon/encrypt
copying build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt/wzipfile.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon/encrypt
copying build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt/py_apply.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon/encrypt
copying build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt/__init__.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon/encrypt
copying build/lib/wellcommon/encrypt/helper4encrypt.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon/encrypt
copying build/lib/wellcommon/wcv.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
copying build/lib/wellcommon/log.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
copying build/lib/wellcommon/com4gps.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
copying build/lib/wellcommon/__init__.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
copying build/lib/wellcommon/helper4file.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
copying build/lib/wellcommon/com.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
copying build/lib/wellcommon/helper4str.py -> build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon
running install_egg_info
running egg_info
creating wellcommon.egg-info
writing wellcommon.egg-info/PKG-INFO
writing dependency_links to wellcommon.egg-info/dependency_links.txt
writing top-level names to wellcommon.egg-info/top_level.txt
writing manifest file 'wellcommon.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
reading manifest file 'wellcommon.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
writing manifest file 'wellcommon.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
Copying wellcommon.egg-info to build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon-1.0-py3.6.egg-info
running install_scripts
creating build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel/wellcommon-1.0.dist-info/WHEEL
creating 'dist/wellcommon-1.0-py3-none-any.whl' and adding 'build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheel' to it
adding 'wellcommon/__init__.py'
adding 'wellcommon/com.py'
adding 'wellcommon/com4gps.py'
adding 'wellcommon/helper4file.py'
adding 'wellcommon/helper4str.py'
adding 'wellcommon/log.py'
adding 'wellcommon/wcv.py'
adding 'wellcommon/encrypt/__init__.py'
adding 'wellcommon/encrypt/helper4encrypt.py'
adding 'wellcommon/encrypt/py_apply.py'
adding 'wellcommon/encrypt/wzipfile.py'
adding 'wellcommon-1.0.dist-info/METADATA'
adding 'wellcommon-1.0.dist-info/WHEEL'
adding 'wellcommon-1.0.dist-info/top_level.txt'
adding 'wellcommon-1.0.dist-info/RECORD'
removing build/bdist.linux-x86_64/wheelpython3 setup.py bdist_wheel命令是直接生成了whl文件,我们后面再说别的命令也能办同样的事情。 经过一长串的输出之后,我们来看看有没有打包成功。
- 查看打包后的文件。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# ls
build dist setup.py wellcommon wellcommon.egg-info当打包命令执行后,会在setup.py文件的同级目录中生成3个文件(夹)build、dist、wellcommon.egg-info,我们只需要关注dist目录即可。让我们cd进去看看都是啥东西:
[root@r zhaopeng]# ls dist/
wellcommon-1.0-py3-none-any.whl没错,wellcommon-1.0-py3-none-any.whl就是我们想要的东西,你把这个文件拷贝到任意python环境使用pip命令安装即可。
pip install wellcommon-1.0-py3-none-any.whl此时,这个包就安装在了你Python的安装目录中的Lib/site-packages/目录下。 完事。
制作tar包
借着这个机会,就多说点,我们从PYPI上面搜模块,在下载时,通常会给你两个选项让你选择: 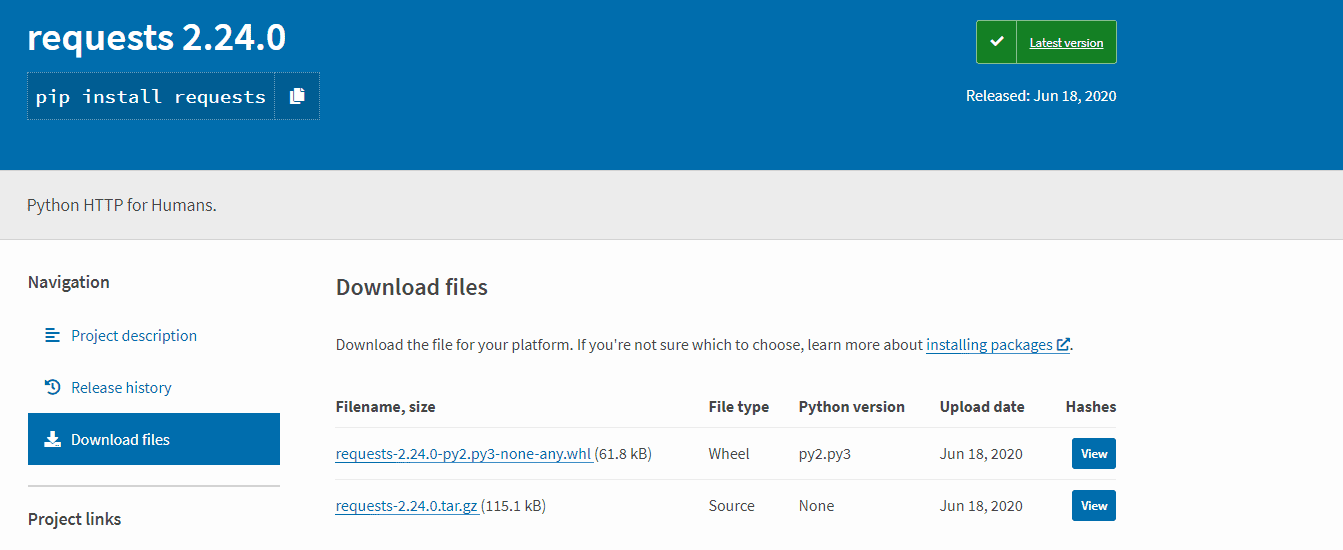 如上图,whl格式目前被认为是Python二进制包的标准格式,下载的到本地需要使用
如上图,whl格式目前被认为是Python二进制包的标准格式,下载的到本地需要使用pip install xxx.whl安装;而tar包则是源码文件,你下载本地解压后就可以看到源码。
那么我们接下来就来聊聊如何制作tar包,然后再制作whl文件。这个跟上面的不冲突,如果你只想要whl文件,用刚才的命令即可:
python setup.py check # 检查setup.py文件是否有问题
python setup.py bdist_wheel # 直接生成whl文件但是,如果你想要tar包,然后还要whl文件,则需要使用下面的命令:
python setup.py check # 检查setup.py文件是否有问题
python setup.py sdist # 主要生成dist文件
pip wheel --wheel-dir=/文件保存的目录 /setup.py文件所在工程目录
# wheel 需要单独下载,pip install wheel来看这几个命令怎么玩的。
- 为了与之前的文件混淆,我将其他文件都删除,恢复到打包之前状态。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# ls
setup.py wellcommon此时,再当前目录下,只有制作好的setup.py和源码包wellcommon。
- 检查
setup.py文件。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# python3 setup.py check
running check
[root@r zhaopeng]#还是刚才的setup.py文件,肯定没问题!
- 生成tar包。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# python3 setup.py sdist
running sdist
running egg_info
creating wellcommon.egg-info
writing wellcommon.egg-info/PKG-INFO
writing dependency_links to wellcommon.egg-info/dependency_links.txt
writing top-level names to wellcommon.egg-info/top_level.txt
writing manifest file 'wellcommon.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
reading manifest file 'wellcommon.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
writing manifest file 'wellcommon.egg-info/SOURCES.txt'
warning: sdist: standard file not found: should have one of README, README.rst, README.txt, README.md
running check
creating wellcommon-1.0
creating wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
creating wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon.egg-info
creating wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon/encrypt
copying files to wellcommon-1.0...
copying setup.py -> wellcommon-1.0
copying wellcommon/__init__.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/com.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/com4gps.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/helper4file.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/helper4str.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/log.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
copying wellcommon/wcv.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon
copying wellcommon.egg-info/PKG-INFO -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon.egg-info
copying wellcommon.egg-info/SOURCES.txt -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon.egg-info
copying wellcommon.egg-info/dependency_links.txt -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon.egg-info
copying wellcommon.egg-info/not-zip-safe -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon.egg-info
copying wellcommon.egg-info/top_level.txt -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon.egg-info
copying wellcommon/encrypt/__init__.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon/encrypt
copying wellcommon/encrypt/helper4encrypt.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon/encrypt
copying wellcommon/encrypt/py_apply.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon/encrypt
copying wellcommon/encrypt/wzipfile.py -> wellcommon-1.0/wellcommon/encrypt
Writing wellcommon-1.0/setup.cfg
creating dist
Creating tar archive
removing 'wellcommon-1.0' (and everything under it)有些warning提示无伤大雅,主要看有没有生成文件。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# ls
dist setup.py wellcommon wellcommon.egg-infopython setup.py sdist命令新生成了dist和wellcommon.egg-info,此时,dist目录内就有了tar包。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# ls dist/
wellcommon-1.0.tar.gz- 有了tar包,再来看怎么生成whl文件。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# pip3 wheel --wheel-dir=/home/zhaopeng/ /home/zhaopeng/
Processing /home/zhaopeng
Building wheels for collected packages: wellcommon
Running setup.py bdist_wheel for wellcommon ... done
Stored in directory: /home/zhaopeng
Successfully built wellcommon看到了Successfully就知道命令执行成功。 现在解释下pip3 wheel --wheel-dir=/home/zhaopeng/ /home/zhaopeng/命令中的两个目录都是啥意思:
--wheel-dir=/home/zhaopeng/,--wheel-dir后跟的目录是生成的whl文件保存的目录。/home/zhaopeng/,空格后的这个目录是这条命令执行的工程目录,pip3 wheel命令会找setup.py文件,所以,工程目录就是setup.py文件所在的目录。
现在,在setup.py文件的同级目录内就有了whl文件。
[root@r zhaopeng]# pwd
/home/zhaopeng
[root@r zhaopeng]# ls
dist setup.py wellcommon wellcommon-1.0-py3-none-any.whl wellcommon.egg-infoOK,现在whl文件也有了,完事。
小结
整篇博客整理下来,也对这几个命令有了更多的了解:
python setup.py check # 用来校验setup.py文件的正确性
python setup.py sdist # 主要生成dist文件
python setup.py bdist_wheel
pip wheel --wheel-dir=/文件保存的目录 /setup.py文件所在工程目录python setup.py check这个就不用说了,无论是制作tar包还是whl文件都要先检查。 现在来看别的命令:
python setup.py bdist_wheel
pip wheel --wheel-dir=/文件保存的目录 /setup.py文件所在工程目录这两个命令都可以单独使用,都是用来生成whl文件的,区别是:
bdist_wheel命令是编译生成,会产生build、dist、wellcommon.egg-info三个文件(夹),而whl文件则在dist目录内。wheel命令则更直接,不会产生中间文件,一步到位生成whl文件。
而python setup.py sdist则是用来打包源码包的,该命令会生成dist目录(而源码包也在该目录内)、wellcommon.egg-info文件。
说到这,暂时没啥补充的了。
see also:
Python 第三方包制作教程 | python whl是什么文件 | 将python包发布到PyPI和制作whl文件 | 打包Python项目